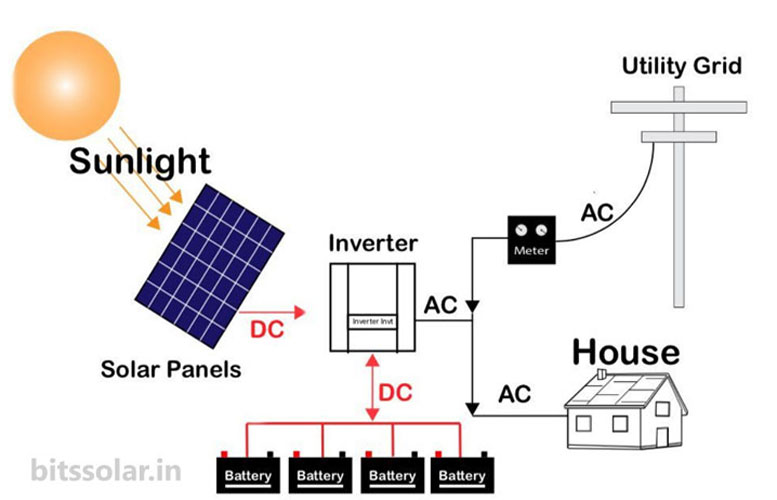
On-Grid Solar System (Grid-Tied System)
An on-grid solar system is connected to the state electricity grid. It does not use batteries; instead, it supplies electricity directly to your home and sends excess electricity to the grid.
How It Works:
- Solar panels capture sunlight and generate DC electricity.
- The grid-tie inverter converts DC to AC electricity.
- Your home uses solar electricity first.
- Excess electricity is sent to the grid via net metering.
- At night or during cloudy days, electricity is automatically drawn from the grid.
Benefits:
- Lower electricity bills: Use free solar electricity first.
- Net metering: Earn credits/money for excess energy.
- Low installation cost: No expensive batteries needed.
-
High efficiency: Direct use of solar power, minimal energy loss.
-
Eco-friendly: Reduces carbon footprint.
-
Government incentives: Subsidies and tax benefits.
Limitation:
- Does not supply electricity during power cuts.
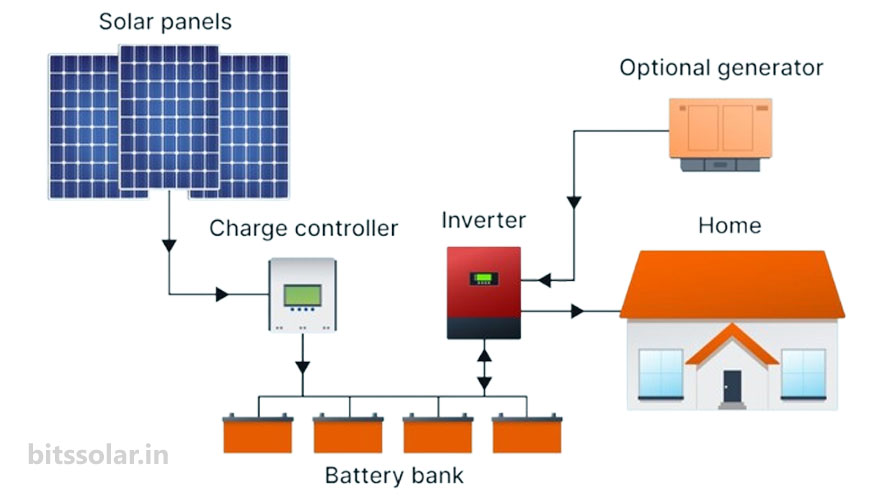
Off-Grid Solar System (Standalone System)
An off-grid system is not connected to the electricity grid. It uses batteries to store energy so you can use electricity anytime.
How It Works:
-
Solar panels generate DC electricity.
-
A charge controller regulates battery charging.
-
Batteries store electricity for night or cloudy days.
-
An inverter converts DC to AC for home appliances.
Benefits:
-
Works in remote areas: No grid required.
-
Continuous power supply: Works during outages.
-
Energy independence: Fully self-sufficient.
Limitation:
-
Higher initial cost (batteries are expensive).
-
Battery maintenance required.
-
Limited backup depending on battery capacity.
Hybrid Solar System (On-Grid + Off-Grid Backup)
A hybrid system combines the features of on-grid and off-grid systems. It is connected to the grid and uses batteries for backup.
How It Works:
-
Solar panels generate DC electricity.
-
AC inverter converts it to AC for your home.
-
Excess electricity charges batteries and/or goes to the grid.
-
During a grid power cut, the system uses battery backup to supply electricity.
Benefits:
-
Uninterrupted power supply – works even during outages.
-
Savings + backup – reduces electricity bills and stores extra energy.
-
Net metering – can export unused energy to the grid.
-
Eco-friendly & cost-effective long-term – best of both worlds.
Limitation:
-
Higher initial cost compared to on-grid or off-grid alone.